int* ptr_a, ptr_b;同
int *ptr_a;
int ptr_b;相等
The right-left rule for reading C declarations
指针的加减部分
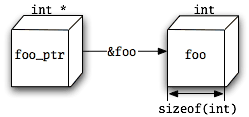
Well, the type of a pointer matters. The type of the pointer here is int. When you add to or subtract from a pointer, the amount by which you do that is multiplied by the size of the type of the pointer. In the case of our three increments, each 1 that you added was multiplied by sizeof(int).
Multiple indirection
int a = 3;
int *b = &a;
int **c = &b;
int ***d = &c;There is no string type in C.
char str[] = "I am the Walrus";This array is 16 bytes in length: 15 characters for “I am the Walrus”, plus a NUL (byte value 0) terminator. In other words, str[15] (the last element) is 0. This is how the end of the “string” is signaled.
size_t strlen(const char *str) { Note the pointer syntax here
size_t len = 0U;
while(*(str++)) ++len;
return len;
}Note the use of pointer arithmetic and dereferencing. That’s because, despite the function’s name, there is no “string” here; there is merely a pointer to at least one character, the last one being 0.